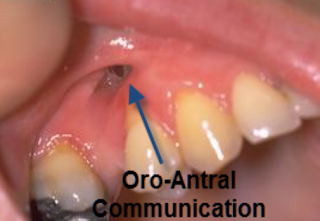
What is an Oro-Antral Communication (OAC)?
This is a communication between the maxillary sinus /
antrum and the oral cavity / mouth.
What is an Oro-Antral Fistula?
If an OAC is not treated, this can become lined with epithelium (skin). Hence, an oro-antral fistula is an epithelised tract linking the maxillary sinus to the mouth;
the tract becomes 'permanent'.
(Alternative names for an OAC / OAF include oro-antral & oral fistulæ, sinus perforations and antra-oral fistulæ).
When an OAC is created, it allows the flow of food,
smoke or fluid from the mouth into the nose - not just
these but also bacteria, fungi and viruses. This can set up
a maxillary sinusitis, which depending on how long the
communication lasts for, may either yield an acute /
chronic maxillary sinusitis.
Causes of OAC’s:
The vast majority of OAC's are created when upper
molars and premolars are removed (almost 50%),
tumours (18.5%), bone infections (osteomyelitis) (11%),
operations to access the maxillary sinus (Caldwell-Luc procedures) (7.5%), trauma (7.5%), dentigerous cysts
(3.7%), correction of septal perforations (3.7%),
perforation of the sinus floor from the tooth socket when
trying to remove an upper tooth and localised florid gum
disease (HIV-related periodontitis) or tooth-tip infections
(chronic apical infection).
Predictive Factors:
As a very broad generalisation, the following may be
thought to predispose to an OAC being formed:
Treatment of the Acute OAF:
If an OAC has been created, then:
How to Recognise the Chronic OAC / OAF:
The OAC is likely to become chronic if:
This is a communication between the maxillary sinus /
antrum and the oral cavity / mouth.
What is an Oro-Antral Fistula?
If an OAC is not treated, this can become lined with epithelium (skin). Hence, an oro-antral fistula is an epithelised tract linking the maxillary sinus to the mouth;
the tract becomes 'permanent'.
(Alternative names for an OAC / OAF include oro-antral & oral fistulæ, sinus perforations and antra-oral fistulæ).
When an OAC is created, it allows the flow of food,
smoke or fluid from the mouth into the nose - not just
these but also bacteria, fungi and viruses. This can set up
a maxillary sinusitis, which depending on how long the
communication lasts for, may either yield an acute /
chronic maxillary sinusitis.
Causes of OAC’s:
The vast majority of OAC's are created when upper
molars and premolars are removed (almost 50%),
tumours (18.5%), bone infections (osteomyelitis) (11%),
operations to access the maxillary sinus (Caldwell-Luc procedures) (7.5%), trauma (7.5%), dentigerous cysts
(3.7%), correction of septal perforations (3.7%),
perforation of the sinus floor from the tooth socket when
trying to remove an upper tooth and localised florid gum
disease (HIV-related periodontitis) or tooth-tip infections
(chronic apical infection).
Predictive Factors:
As a very broad generalisation, the following may be
thought to predispose to an OAC being formed:
- Proximity of sinus / tuberosity
- Thickened tooth cement / tooth fused to jaw bone
- Infected teeth / long-standing decay
- Marked periodontitis / gum disease
- Lone-standing
- Previous history of OAC’s.
Treatment of the Acute OAF:
If an OAC has been created, then:
- Do not probe the defect
- Promote good blood clot
- The gingival / gum margins around the socket should be approximated as close as possible
- Physical agents placed in the socket to stop excess bleeding (Surgicel, Spongostan or Haemocollagene)
- Antibiotics should be prescribed (Amoxycillin, Doxycycline)
- Nasal decongestants can be used (Ephedrine nasal drops, Oxymetazoline)
- Steam inhalations can be used (Menthol & Eucalyptus)
- Antiseptic mouth-wash should be used (Corsodyl)
- No nose-blowing or smoking
How to Recognise the Chronic OAC / OAF:
The OAC is likely to become chronic if:
- OAC is greater than 5mm in diameter
- Gingival tissues / gums around the socket can’t be approximated
- Post-op régime is not followed
- Wound dehiscence / breakdown
- Enucleation of a dental / dentigerous cyst
- May develop 4 – 6 weeks post-extraction
- Problems with smoking, eating or drinking
- Cacogeusia / foul taste
- Chronic maxillary sinusitis
- Antral polyp herniating into the mouth
- Purulent (pus) discharge from nose


Amazing geet. Keep it up
ReplyDelete